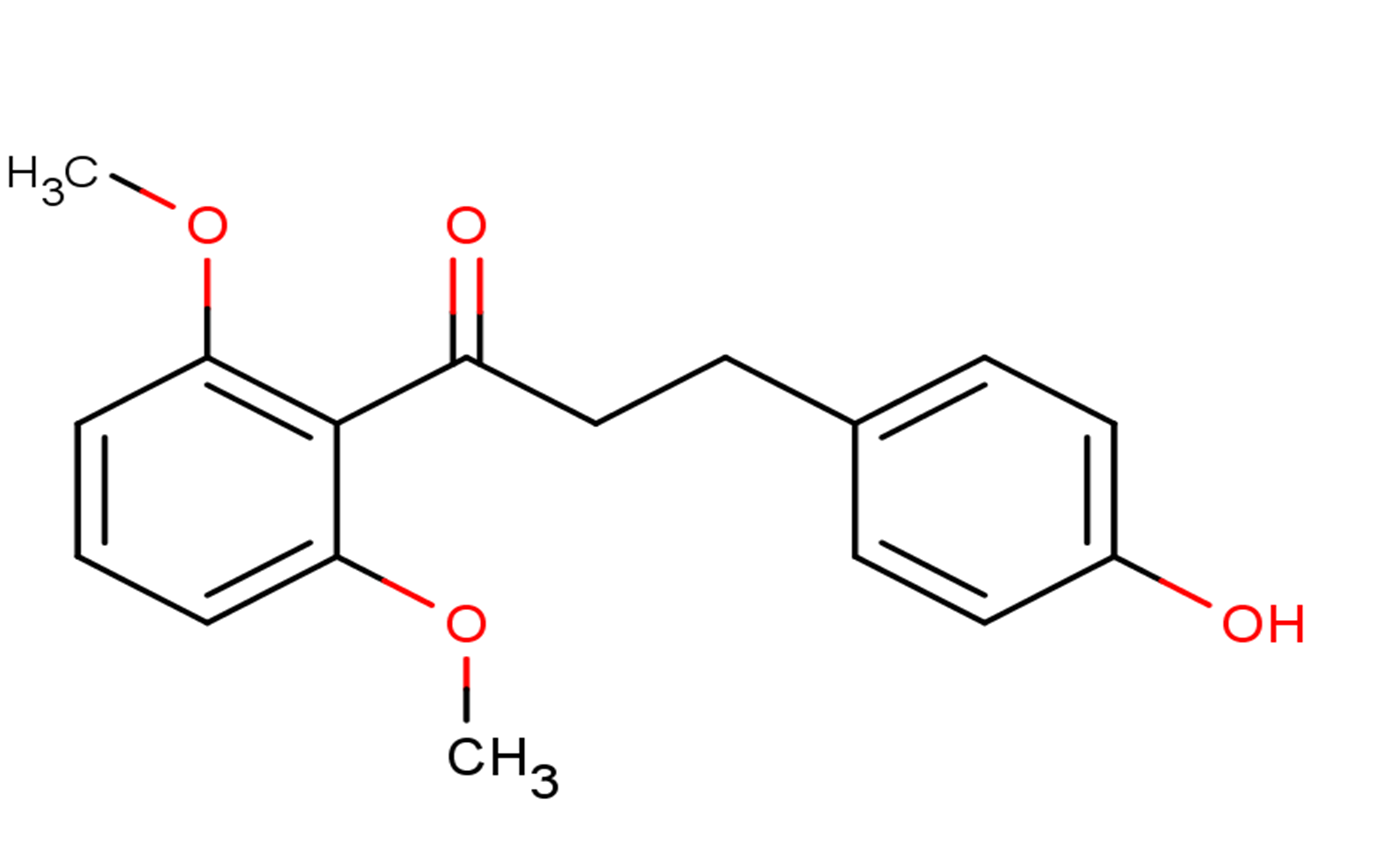
Cochinchinenin A
CAS No. 221696-69-1
Cochinchinenin A( —— )
Catalog No. M24002 CAS No. 221696-69-1
Cochinchinenin A is the material basis for the analgesic effect of Dragons Blood.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 141 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 205 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 347 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 516 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 740 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCochinchinenin A
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCochinchinenin A is the material basis for the analgesic effect of Dragons Blood.
-
DescriptionCochinchinenin A is the material basis for the analgesic effect of Dragons Blood.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number221696-69-1
-
Formula Weight286.3
-
Molecular FormulaC17H18O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM
-
SMILESCOC1=C(C(=CC=C1)OC)C(=O)CCC2=CC=C(C=C2)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
Modulation of dragon??s blood on tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium currents in dorsal root ganglion neurons and identification of its material basis for efficacy Science in China Series C June 2006, Volume 49, Issue 3, pp 274-285
molnova catalog



related products
-
Deltaline
Use of Deltaline as versatile antidotes against poisoning of animals and humans.
-
[Leu31,Pro34]-Peptid...
[Leu31,Pro34]-Peptide YY (human)
-
(-)-Benzotetramisole
(-)-Benzotetramisole makes an efficient and selective catalyst. (-)-Benzotetramisole is a benzannulated derivative of the anthelmintic compound tetraimidazole 3 and is itself an effective catalyst for conversion.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


